Writing a blog post after a long time.. This time on Cloud Computing fundamentals..
Why Cloud Computing?
The IT challenges listed below have made organizations think about the Cloud Computing model to provide better service to their customers
- Globalization: IT must meet the business needs to serve customers world-wide, round the clock - 24x7x365.
- Aging Data Centers: Migration, upgrading technology to replace old technology.
- Storage Growth: Explosion of storage consumption and usage.
- Application Explosion: New applications need to be deployed and their usage may scale rapidly, The current data center infrastructures are not planned to accommodate for such rapid growth.
- Cost of ownership: Due to increasing business demand, the cost of buying new equipment's, power, cooling, support, licenses, etc., increases the Total Cost of Ownership(TCO.)
- Acquisitions: When companies are acquired, the IT infrastructures of the acquired company and the acquiring company are often different. These differences in the IT infrastructures demand significant effort to make them inter-operable.
What is Cloud computing? (Definition): According to NIST, Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
What are the Essential Characteristics?
Cloud computing should have all of the following characteristics
- On-Demand Self-Service
- Resource Pooling
- Rapid Elasticity
- Measured Service
- Broad Network Access
What are the building blocks of Cloud Computing?
What are the Service Models in Cloud Computing?
- Infrastructure as a service
- Platform as a service
- Software as a service
What are the Deployment Models in Cloud Computing?
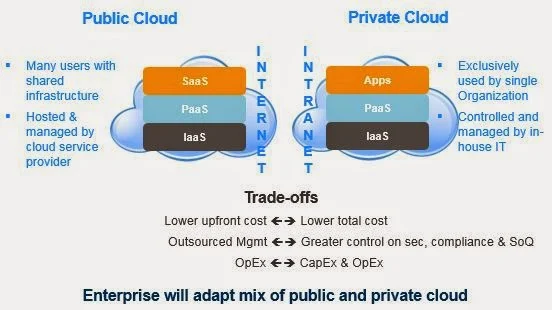
- Public Cloud: Infrastructure Shared across multiple end users which may include companies
- Private Cloud : Exclusive for one company, it can be on-premise / exclusively hosted at cloud service provider
- Hybrid Cloud : Combination of Public and Private cloud
- Community Cloud : Set of similar types of customer, comes together and share infrastructure, example multiple universities contribute and use one cloud infrastructure.
What is the difference between public and private cloud?
Finally, what are the befits and challenges ?
Benefit
Consumer Challenges
- Security and Regulations
- Quality of service
- Network Latency
- Supportability
- Long term cost
- Lock-in
Providers Challenges
- Service Warranty and service cost
- Huge number of s/w to manage
- No standard cloud access interface